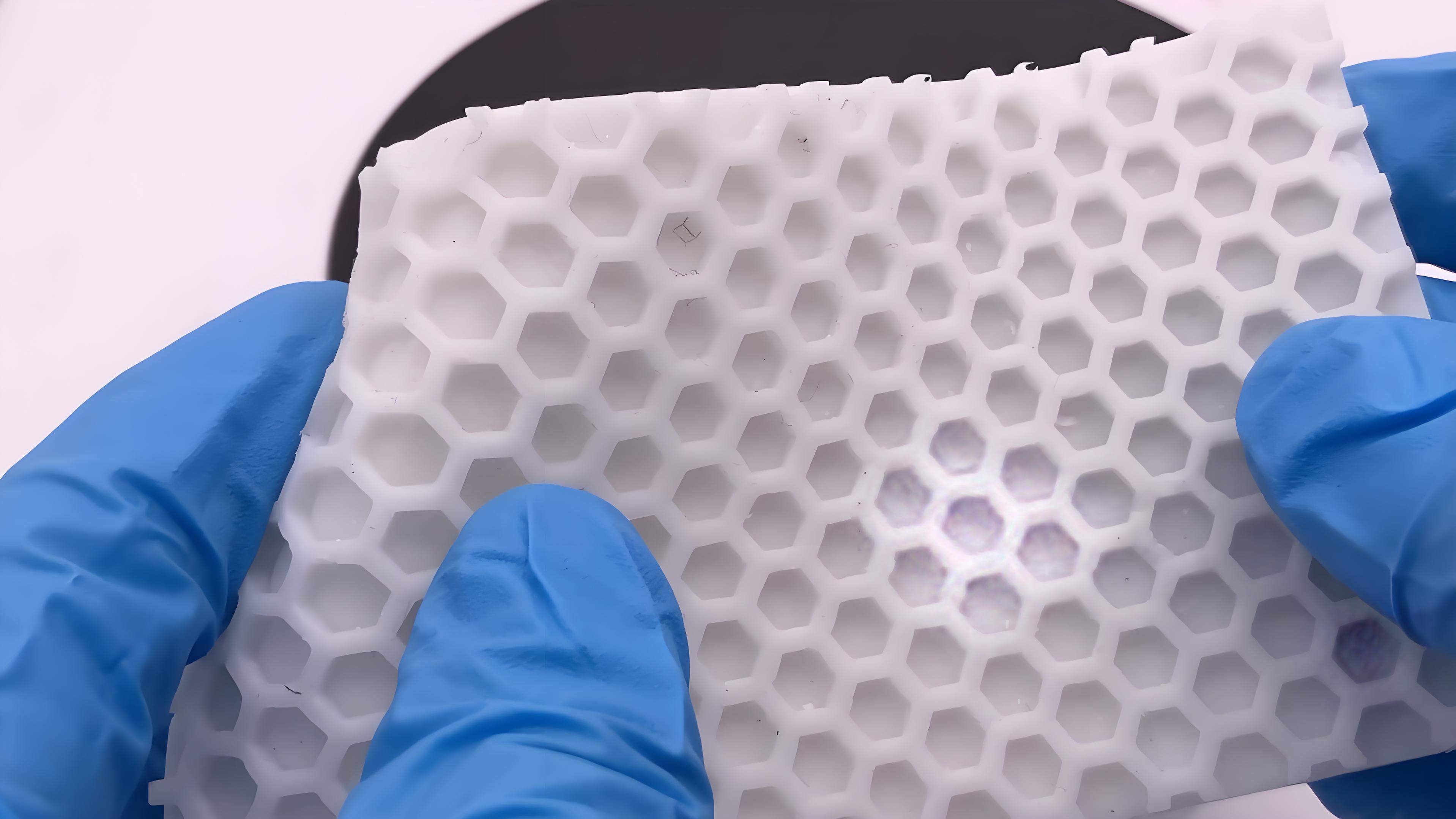
After molding, molded silicone products usually need a series of post-processing processes to improve product performance, appearance or meet specific functional requirements. The following are common post-molding processing processes and detailed descriptions:
1. Burr treatment (deburring/trimming)
Reason: Flash or burrs will be generated at the overflow or parting line during the molding process.
Method:
Manual trimming: Use scissors, blades or special tools to manually remove burrs, suitable for small batches or precision products.
Frozen deburring: Freeze the product (such as below -30℃) to make the silicone brittle, and remove the burrs by vibration or sandblasting, suitable for complex shapes or batch production.
Mechanical punching: Use stamping dies or automated equipment to remove burrs in batches, which is efficient but requires customized molds.
Precautions: Avoid excessive trimming that may cause product breakage or dimensional deviation.
2. Secondary vulcanization (post-curing)
Purpose: Remove residual volatiles, increase the cross-linking density of silicone, and enhance mechanical properties and temperature resistance.
Process parameters:
Temperature: 180-200℃ (adjusted according to the type of silicone).
Time: 2-4 hours.
Equipment: Oven or vulcanization tank, uniform temperature control is required.
Effect: Reduce odor, improve tensile strength, resilience and chemical stability.
3. Surface treatment
Spraying/coating:
Functional coating: spray antistatic, hydrophobic or flame retardant coating.
Decorative coating: add color or matte/gloss effect, special silicone ink is required.
Screen printing: print logo, text or pattern, need to pass adhesion test.
Laser engraving: precision engraving logo or texture, non-contact processing, suitable for high precision requirements.
Plasma treatment: improve surface energy, enhance bonding or printing adhesion.
4. Cleaning and inspection
Cleaning:
Ultrasonic cleaning: remove surface dust or mold release agent residue.
Solvent wiping: clean with solvents such as isopropyl alcohol.
Inspection:
Appearance inspection: no bubbles, glue deficiency, stains or burrs.
Dimension detection: caliper, projector or three-coordinate measurement.
Performance test: hardness (Shore A), tensile strength, tear strength, aging resistance, etc.
5. Special post-processing
Bonding and assembly:
Bonding silicone with metal/plastic: use primer to enhance the bonding strength, and use silicone glue (such as RTV glue).
Mechanical fixation: embed metal parts or screws.
Function modification:
Conductive treatment: add conductive filler or plating.
Antibacterial treatment: add antibacterial agent or surface coating.
6. Packaging and storage
Dust-proof packaging: prevent silicone from absorbing dust.
Anti-sticking treatment: sheet products need to be placed in layers to prevent adhesion.
Environmental requirements: avoid light and moisture, and the storage temperature is recommended to be 10-25℃.
Key points
Process sequence: usually deburring → cleaning → secondary vulcanization → surface treatment → inspection.
Temperature control: secondary vulcanization needs to be heated/cooled slowly to avoid deformation caused by thermal stress.
Environmental requirements: some processes (such as solvent cleaning) must comply with VOCs emission standards.
By reasonably selecting post-processing technology, the quality and added value of molded silicone products can be significantly improved to meet the stringent requirements of medical, electronic, automotive and other fields. In practical applications, the process needs to be comprehensively optimized according to product use and cost.